Hello Folks,
You would have seen in my previous article post, about the XPath and Value() XML methods. If you want to refer it again, just follow the link;
Well in this post, I would like to deal with nodes (), exist (), query (), and modify () methods.
Nodes ():
- The nodes () method returns a row set representation of the XML document.
- The nodes () method is useful when you want to shred an xml data type instance into relational data.
- It also allows you to identify nodes that will be mapped into a new row.
- Every xml data type instance has an implicitly provided context node. For the XML instance stored in a column or variable, this is the document node. The document node is the implicit node at the top of every xml data type instance.
- The result of the nodes () method is a row-set that contains logical copies of the original XML instances.
- You can also retrieve multiple values from the row-set by applying value () method to the row-set returned by nodes () and retrieve multiple values from the original XML instance.
- The Syntax can be seen as:
nodes (XQuery) as Table(Column)
- An XQuery expression operation can be performed on each node returned by the nodes () method.
- The following example will make you clear about the nodes () method:
The following query returns an accessor to all the S_Id elements in the XML documents and applies the value () method on each node:
DECLARE @a XML
SELECT @a = '
<Students>
<S_Id>01</S_Id>
<S_Id>02</S_Id>
<S_Id>03</S_Id>
<S_Id>04</S_Id>
</Students>'
SELECT a.value('.','CHAR(2)') AS S_ID
FROM @a.nodes('/Students/S_Id') T(a)
The result can be seen as:
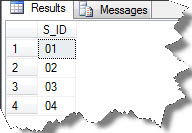
Now, the following example is a modified version of the preceding query that reads information from an XML column:
IF OBJECT_ID('StudXML', 'U') IS NOT NULL DROP TABLE StudXML
CREATE TABLE StudXML(S_ID INT, StudData XML)
GO
INSERT INTO StudXML(S_ID, StudData)
SELECT 1, '<Student S_ID = "1">
<Subject Sub_ID = "20A" Sub_Marks = "100" />
<Subject Sub_ID = "20B" Sub_Marks = "100" />
</Student>'
INSERT INTO StudXML(S_ID, StudData)
SELECT 2, '<Student S_ID = "2">
<Subject Sub_ID = "20C" Sub_Marks = "100" />
<Subject Sub_ID = "20D" Sub_Marks = "100" />
</Student>'
SELECT S_ID, a.value('@Sub_ID', 'CHAR(3)') AS Sub_Id
FROM StudXML
CROSS APPLY StudData.nodes('/Student/Subject') o(a)
The result can be seen as:
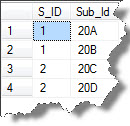
Note: The CROSS APPLY operator joins each node returned by the nodes () method with the table, and the value () method reads the Sub_Id value from each element returned by the nodes () method.
Exist ():
- The exist() method checks whether an element or attribute specified by a given XPath expression exists in the document.
- It returns 1, representing True, if the XQuery expression in a query returns a nonempty result. That is, it returns at least one XML node.
- It returns 0, representing False, if it returns an empty result.
- The Syntax for this is: exist (XQuery)
- This will become more clear to you if you see the following query:
SELECT S_ID FROM StudXML
WHERE StudData.exist('/Student/Subject[@Sub_ID = "20C"]')= 1
The result can be seen as:

Query ():
- The query () method takes an XQuery expression and evaluates it to a list of XML elements that can be accessed and processed further.
- The result is of xml type. The method returns an instance of untyped XML.
- The Syntax can be seen as:
query (‘XQuery’)
- This will become more clear, if you see the following example:
DECLARE @Doc xml
SET @Doc = '<Root>
<StudentDetails S_ID="1" StudName="Piyush Bajaj">
<Subjects>
<Maths>2 books for reference</Maths>
<Physics>3 books for reference</Physics>
</Subjects>
</StudentDetails>
</Root>'
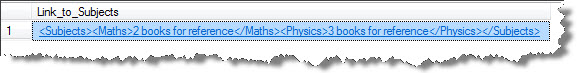
SELECT @Doc.query('/Root/StudentDetails/Subjects') AS Link_to_Subjects
The result can be seen as:
Modify ():
- The modify () method is used to perform XML DML operations on an XML document.
- It allows inserting, updating, or deleting XML elements or attributes within an XML document.
- The modify() method of the xml data type can only be used in the SET clause of an UPDATE statement.
- The Syntax can be seen as:
modify (XML_DML)
- An error is returned if the modify() method is called on a null value or results in a null value.
Well, this was all about XML Data Type Methods.
Hope you got it understood well 🙂
And also comments on this!!
Regards
Piyush Bajaj
Like us on FaceBook | Follow us on Twitter | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
Follow me on Twitter | Follow me on FaceBook
