Yes, a SQL Server database can be case sensitive. Case sensitive here means that SQL Server will return different result set for CASE, Case, CaSe etc. and it will treat the mentioned strings as 3 different strings. A case sensitive database has a case sensitive collation. In this blog we’ll look at case sensitive searches. A list of collation is given here
Let’s consider an example
USE Adventureworks2014
GO
SELECT businessentityid,
firstname
FROM person.person
WHERE firstname LIKE 'terri%'
The above query does a search on Person.Firstname column. The output of above query is given below.
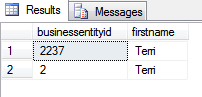
The firstname in above results is Terri whereas the search value is terri. The SQL Server does a case insensitive search. Let’s now change the collation of Person.Firstname column to case sensitive collation.
-- might need to drop an index on firstname -- column if it exits ALTER TABLE Person.Person ALTER COLUMN Firstname NVARCHAR(100) COLLATE Latin1_General_CS_AS
Let’s now do the search and observe the result.
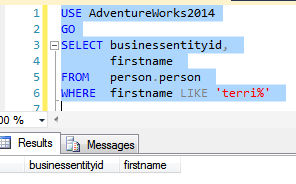
The query returns zero results as SQL server is now doing a case sensitive search. Let’s change the case of the search value to that of the value in Person.Firstname column and do a search
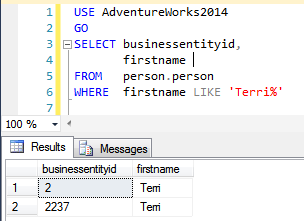
The SQL server does a case sensitive search and founds 2 matching rows.
Let’s now do a case insensitive search on a case sensitive column without changing the column collation
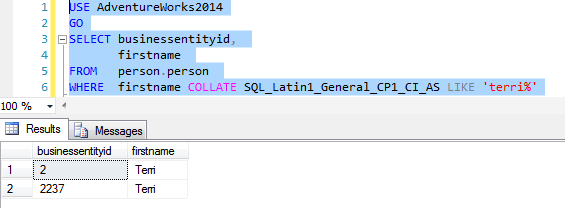
The word COLLATE sets the collation of Person.Firstname column to case insensitive and thus SQL server performs case insensitive search returning 2 rows.
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
