THE QUOTED_IDENTIFIER setting allows SQL Server to follow ISO rules regarding quotation mark delimiting identifiers and literal settings or in plain English it specifies how SQL Server treats data with in single or double quotes. When its ON the SQL Server treats anything inside double quotes as SQL Server object and anything with single quotes as literal and when it is OFF anything with in single and double quote is treated as literal. Let’s understand this with an example.
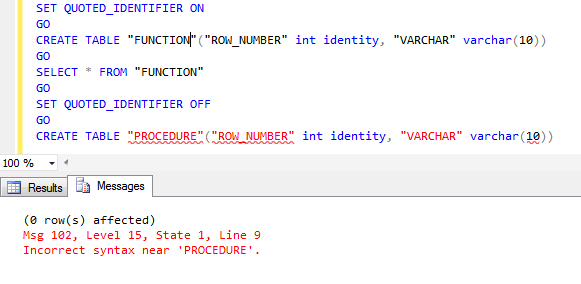
In above snapshot, a table with reserved keyword FUNCTION is created with QUOTED_IDENTIFIER set to ON and the query to create a table with reserved keyword PROCEDURE fails with QUOTED_IDENTIFIER set to OFF.
Let’s see the behavior of QUOTED_IDENTIFIER setting on select statement.
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO SELECT 'FUNCTION' AS QI_ON GO SELECT "FUNCTION" AS QI_ON
The first select works and the second fails.
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF GO SELECT 'FUNCTION' AS QI_ON GO SELECT "FUNCTION" AS QI_ON
Both the select queries work well.
The default value of QUOTED_IDENTIFIER is ON.
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
