A cursor is a way to iterate each row one by one in a SQL Server table. Although, T-SQL is a set based language however, many a times need arises to do row by row operations. Below is a simple cursor in SQL Server to select values from a table.
--simple cursor in sql server Declare @orderid int, @orderqty int -- declare a cursor DECLARE sample_cursor CURSOR FOR SELECT SalesOrderId,OrderQty from Sales.SalesOrderDetail -- open cursor and fetch first row into variables OPEN sample_cursor FETCH NEXT FROM sample_cursor into @orderid,@orderqty -- check for a new row WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS=0 BEGIN -- do complex operation here PRINT 'Order ID: ' + CAST(@orderid as varchar(12)) + ' Order Qty: ' + CAST(@orderqty as varchar(12)) -- get next available row into variables FETCH NEXT FROM sample_cursor into @orderid,@orderqty END close sample_cursor Deallocate sample_cursor
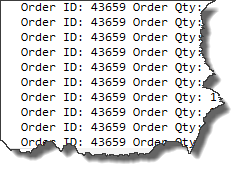
The query declares a sample_cursor to iterate through Sales.SalesOrderDetail table. The @@Fetchstatus function returns the status of the last cursor FETCH against a cursor, where 0 means successful, -1 is failed or row is not in result set and -2 means that row fetched is not present in the cursor. Thus, we can iterate through a cursor while @@Fetchstatus =0. The complex operation is done inside the while loop. The example shown here is just to explain the cursor; it doesn’t perform any complex operation.
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
