Below is a SQL query to find table size in SQL Server. The calculation is based on SQL Query to find row size SQL Server blog (give the link of the said blog).
IF object_id('sp_GetTableSize') is not null
drop procedure sp_GetTableSize
GO
CREATE procedure sp_GetTableSize(@Tablename varchar(100))
AS
BEGIN
declare @dynamicsql varchar(1000)
-- A @pkcol can be used to identify max/min length row
set @dynamicsql='SELECT ''' + @Tablename + ''' AS TableName,SUM(rowsize) AS TableSize_Bytes FROM (SELECT 0'
-- traverse each record and calculate the datalength
select @dynamicsql = @dynamicsql + ' + isnull(datalength(' + name + '), 1)'
from syscolumns where id = object_id(@Tablename)
set @dynamicsql = @dynamicsql + ' as rowsize from ' + @Tablename + ')a'
exec (@dynamicsql)
END
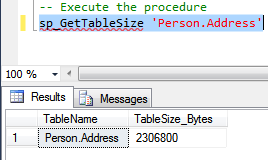
The above query creates a procedure sp_GetTableSize procedure. The procedure accepts a parameter @Tablename, the table to calculate the size for. Execute the procedure to get the table size in bytes.
-- Execute the procedure sp_GetTableSize 'Person.Address'
Another way to get table size is the “sp_spaceused” stored procedure.
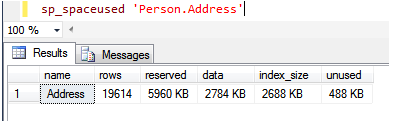
The column description is given below.
Rows: number of rows in a table.
Reserved: the total amount of space allocated by objects in the database.
Data: Total amount of space used by data.
Index_size: Total amount of space used by indexes.
Unused: Total amount of space reserved for objects in the database, but not yet used.
The above description is taken from http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188776.aspx
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
