Hi Friends,
We can control SQL Server query optimizer’s decision by forcing any T-SQL queries to use a specific join type. In today’s post we will explore SQL Server Join hints and their impact on execution plans.
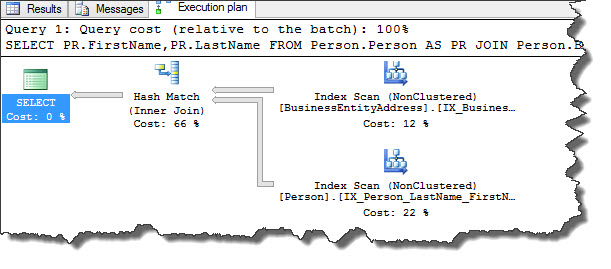
Let us begin with following sql query and see what the default choice of query optimizer is.
USE [AdventureWorks2012] SELECT PR.FirstName,PR.LastName FROM Person.Person AS PR JOIN Person.BusinessEntityAddress BE ON PR.BusinessEntityID = BE.BusinessEntityID
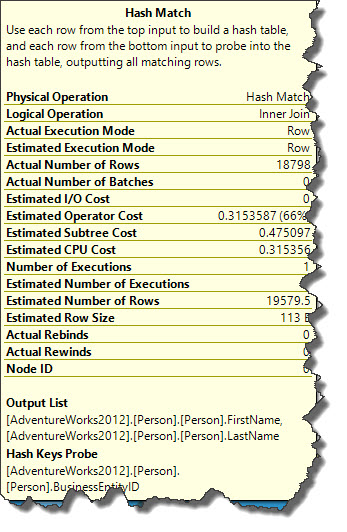
Hash Match join is the optimum and efficient plan operator for the statement(s) used in our example according to SQL Server query optimizer. We can force optimizer to use any of the available join algorithms i.e. Hash Joins, Merge Joins (read here Part1, Part2) or Nested Loop (read here Part1, Part2) Joins at query level or at join level using Join Hints. Let’s do that now.
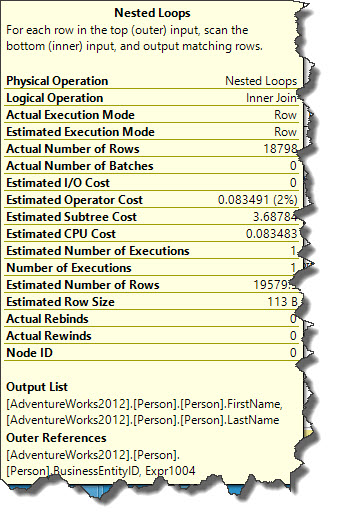
USE [AdventureWorks2012] SELECT PR.FirstName,PR.LastName FROM Person.Person AS PR JOIN Person.BusinessEntityAddress BE ON PR.BusinessEntityID = BE.BusinessEntityID OPTION (LOOP JOIN)
In the example query optimizer decided to choose Hash Join in the normal circumstances but we forced optimizer to exclude Hash Join and to use Nested Loop Join. This operation reduced Estimated Operator Cost from 66% (in Hash Join Operator) to 2% and Estimated Subtree Cost has changed from 0.47 to 3.6. Estimated Operator Cost and Estimated Subtree Cost values may change when we run statement(s) used in this example on different systems running on different configurations.
Note: This is just an illustration and you should never ever try this method in your live systems.
You can read all blogs in One operator a day series by clicking here and here is the Index for my execution plan series.
Happy Learning!
Regards,
Kanchan
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook | Follow me on Twitter | Follow me on FaceBook