Hi Friends,
SQL Server Merge Join operator performs the inner join, left outer join, left semi join, left anti semi join, right outer join, right semi join, right anti semi join, and union logical operations and is a physical operator. A merge operator can be used only when both sets of rows are pre-sorted according to the join expression(s).
Let’s take an example of merge join operator.
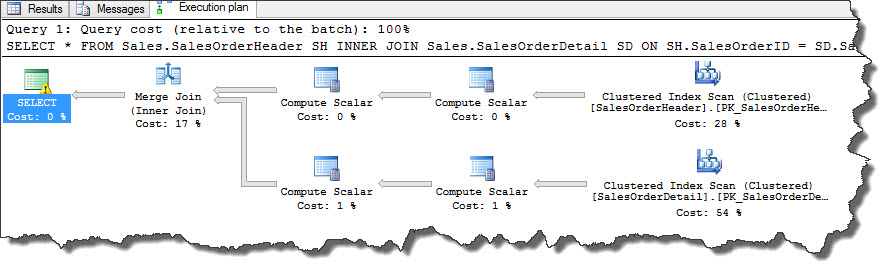
USE [AdventureWorks2012] SELECT * FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader SH INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderDetail SD ON SH.SalesOrderID = SD.SalesOrderID
According to the above execution plan, SQL Server query optimizer performed a Clustered Index Scan on Sales.SalesOrderHeader and Sales.SalesOrderDetail tables as we did not specify a WHERE clause. Query statement in example used clustered index to join two tables and since clustered index sorted in the order of clustered keys, it covers all queries and used to retrieve any column in the table that are specified in SELECT statement.
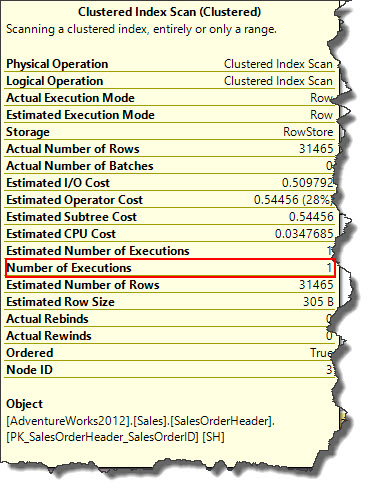
Key difference between a Nested Loop join and Merge join is, in a merge join both input operators are executed only once and we can verify this using ToolTip as shown below.
Bear in mind, when we are selecting all columns, both the tables needs to be loaded in memory and needs to send over network so there could be a performance overhead. This operator combines the advantage of hash match and nested loops which results in low CPU consumption and enables fast output of matched rows for further processing.
We are going discuss more on this operator tomorrow, stay tuned.
Regards,
Kanchan
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook | Follow me on Twitter | Follow me on FaceBook