Hi Friends,
SQL Azure architecture contains four layers that works collectively to provide cloud based relational database. To name them;
- Client Layer
- Services Layer
- Platform Layer
- Infrastructure Layer
These four layers help SQL Azure to work with third-party applications, open source, and many other technologies. This layered architecture is quite similar to on-premises one except services layer which is new to SQL Azure which provides much of the SQL Azure specific DB platform functionality.
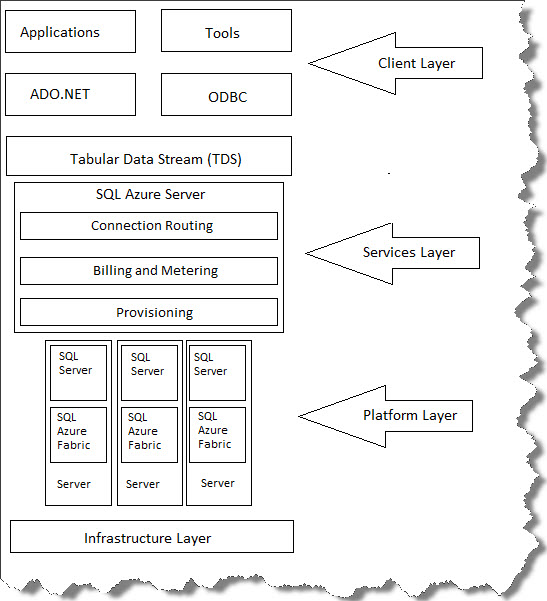
Let us run through each of these layers in short one by one;
Client Layer
Application uses client layer to communicate with SQL Azure. This layer can either reside on-premise or on Windows Azure. SQL Azure uses TDS interface as SQL Server which helps application developers to use different tools and libraries to develop cloud based applications. ADO.NET and other providers are used to get data access and help you to use T-SQL statements and other known technologies.
Services Layer
This is bridge between Client layer and Platform layer and responsible for Provisioning i.e. creating or provisioning databases either through Azure platform or SSMS. Billing and metering i.e. handling usage-based metering and billing different Azure platform accounts. Routing connections i.e. controls all connections routing between physical servers and applications. To sum up, this layer handles connection routing, meter and billing around usage and database creation and provisioning functionality.
Platform Layer
This layer includes multiple physical SQL Instances and services. Each instance is managed by SQL Azure Fabric. Main part of this layer is Azure Fabric, distributed computing systems that installed on each physical SQL Servers with very well integrated networks, storage and servers. Azure fabric is capable of providing load balancing, automatic failovers and replication between different servers.
Infrastructure Layer
This layer represents the physical administration of hardware and OS that support Services layer. In SQL Azure architecture when connecting to any SQL Server, connections are through TDS endpoints via Services layer which then routes connections to the actual physical servers i.e. connections aren’t directly connecting to physical SQL Servers.

One important point to note here is, when you connect to any on-premise SQL Server you typically specify physical server name and instance name but in SQL Azure you will have to specify FQDN like server.database.windows.net etc.
Regards
Kanchan Bhattacharyya
Like us on FaceBook | Follow us on Twitter | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
Follow me on Twitter | Follow me on FaceBook
