ANSI_NULLS and QUOTED_IDENTIFIER are among the most common settings that a DBA/developer may come across in Ansi Null SQL Server. Let’s have a look at these settings in detail.
ANSI_NULLS
This is used to govern NULL comparison. When ON, ISO NULL comparison standard are followed and = and <> operators aren’t used for NULL comparison instead IS NULL and IS NOT NULL are used for NULL comparison. This value is ON by default. Let’s have a look at an example.
SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO CREATE TABLE tblnulls(sno INT IDENTITY,col1 CHAR(1)) GO INSERT INTO tblnulls SELECT 'A' UNION SELECT NULL
The above query sets ANSI_NULLS = ON and creates a table with some dummy values. Let’s do NULL comparison and analyze the results.
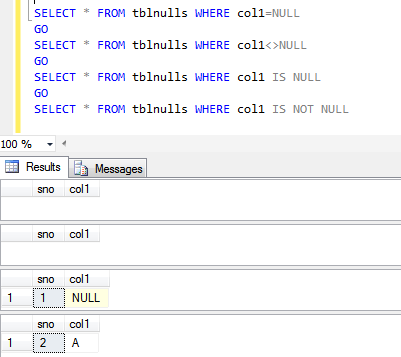
As explained above, the = and <> operators didn’t return any rows whereas IS NULL and IS NOT NULL returned correct results. Let’s now switch ANSI_NULLS to OFF and analyze the resultset.
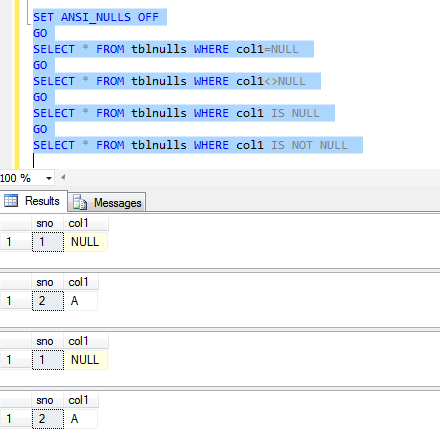
As expected, the = and <> operator return correct result with ANSI_ NULLS OFF.
In future SQL Versions, the ANSI_NULLS will always be ON by default and the setting it to OFF will generate errors.
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook
